About Diamond
Diamonds have been around for thousands of centuries, and have had many different uses, historical moments and so much more. While a true timeline of diamond history could go on forever, below is a short timeline that includes a few significant moments in the history of diamonds.
As the hardest naturally forming material on Earth, a diamond gets its name from the ancient Greek word adámas, which means “unbreakable”. 800-1000 BC; Diamonds are believed to have been first discovered in India, approximately 3000 years ago. 327 BC; Alexander the Great, King of the ancient Greek state Macedon, brings the first diamonds from India to Europe.
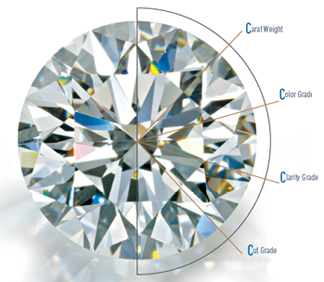
Until the middle of the twentieth century, there was no agreed-upon standard by which diamonds could be judged. The 4Cs of Diamond Quality is the universal method for assessing the quality of any diamond, anywhere in the world.The creation of the Diamond 4Cs meant two very important things: diamond quality could be communicated in a universal language, and diamond customers could now know exactly what they were about to purchase.
4C’s means Color, Clarity, Cut &Carat . The color of diamond means the presence of hue or yellow tint, whilethe clarity of a diamond refers to the size and number of ‘inclusions’ in it.The cut of diamond means the shape of diamond in which it is made into; eg- round, square, oval…etc. The last and the most The Carat means the term used to represent the weight of the diamond.
**All the 4C’s are explained more detail wise on below tabs.
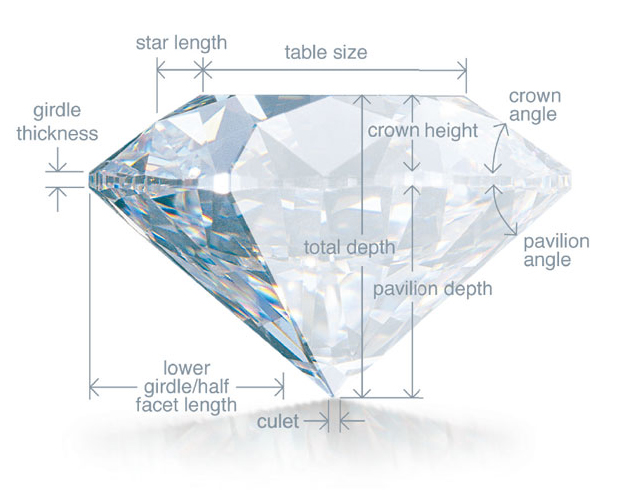
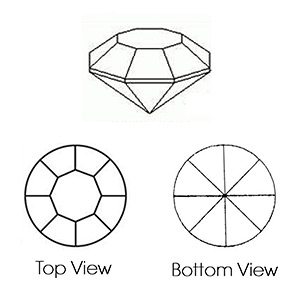
Once cut and polished, all diamonds possess a shared set of characteristics, often referred to as the anatomy of the diamond. From the illustrated image the major terms on anatomy of diamonds are;
Diameter: The width of the diamond as measured through the girdle.
Table: The largest facet of a gemstone.
Crown: The top portion of a diamond extending from the girdle to the table.
Girdle: The intersection of the crown and pavilion which defines the perimeter of the diamond. While generally a minor consideration, Blue Nile recommends avoiding girdles graded either extremely thin, which makes diamonds more susceptible to chipping, or extremely thick, which puts too much weight in the middle of the diamond, causing it to look smaller than diamonds of similar weight.
Pavilion: The bottom portion of a diamond, extending from the girdle to the culet.
Culet: The facet at the tip of a gemstone. The preferred culet is not visible with the unaided eye (graded “none” or “small”).
Depth: The height of a gemstone measured from the culet to the table.

Though diamonds are mined throughout the world, they are majorly found in the Australia, Africa, Russia and Canada mines.A key source of precious ware, diamond mining provides employment as well as health care to thousands Africans.
In April 2003, a law, Kimberley Process Certificate Scheme, was passed that made it mandatory for diamond merchants to purchase diamonds from manufacturers who have documentation that endorsed that the merchandise was acquired through legitimate channels.George Diamonds, follows an international method, KPCS, of tracking and certifying these shiny rocks which are conflict free.
The World Diamond Council created a System of Warranties for diamonds that endorsed that all buyers and sellers of both rough and polished diamonds must make the following affirmative statement on all invoices:
“The diamonds herein invoiced have been purchased from legitimate sources not involved in funding conflict and in compliance with United Nations resolutions. The seller hereby guarantees that these diamonds are conflict free, based on personal knowledge and/or written guarantees provided by the supplier of these diamonds.”(in quotes, so no change)
It is considered an offence to issue a warranty declaration on a sales invoice, unlessthe warranty invoices were received when purchasing. Each company trading in diamonds must also keep records of the warranty invoices when buying or selling diamonds. This flow of warranties were supposed to be audited and reconciled on an yearly basis by the company’s auditors.
In addition, the diamond industry and their members have adopted the following principles of self-regulation:
To trade only with companies that issue warranty declarations on their invoices;
To refuse purchase from suspect sources or unknown suppliers, or the country that have not implemented the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme;
To refuse to purchase diamonds from any sources that have been found to have violated government regulations restricting the trade in conflict diamonds;
To refuse purchase of diamonds from any region that is an advisory to a governmental authority which indicates that conflict diamonds are sourced and available for sale in such region, unless these diamonds have been exported in compliance with the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme;
To knowingly not totrade or assist to trade in conflict diamonds;
To ensure that all company employees that trade diamonds which are within the diamond trade. They are well informed regarding trade resolutions and government regulations restricting the trade in conflict diamonds.
The term Single Cut Diamond or Eight Cut Diamond also known as 8/8 diamonds or eight cut diamonds have 8 facets on the table and 8 facets on the pavilion.
A single cut, is a simple form of cutting a round diamond with only 17 or 18 facets. If compared, a Single Cut Diamond (usually small Carat Weights of 1.2mm or less), to a Full Cut Diamond (58 facets), there is a difference.
Small high quality single cut diamonds are premium especially in the watch industry. This is because there are fewer but larger facetswhich emit colorful light that is diluted in white light of the full cut stones.
Single cut diamonds are sought after for high-end micropave settings. Typically, each stone used in micropave is a full cut diamond, However, full cut diamonds are not to be used in micropave, as the larger facets on a single cut diamond are proportionally bigger and tend to return reflect light and colour.
High quality single cuts are mainly used in expensive watches to mark the hour or decorate the dial. This high demand from the luxury watch industry makes single cut diamonds very rare and expensive in comparison to full cut diamonds. The luxury watch industry consumes virtually the entire annual production.
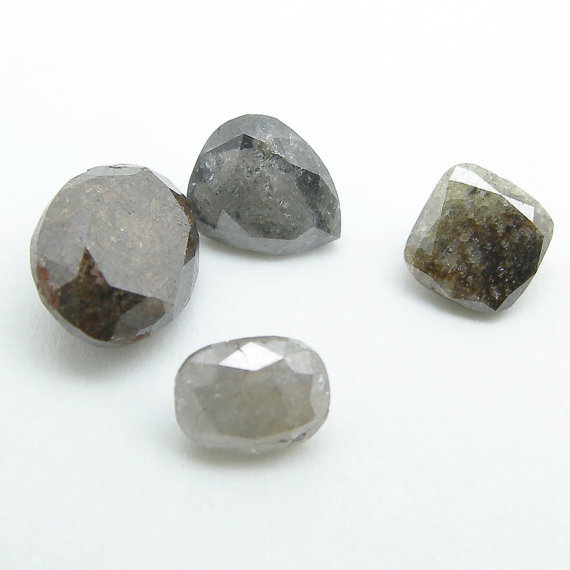

Icy Diamonds are 100% natural diamonds available in the purest form from the earth. They are cut and polished like white diamonds.Icy Diamonds are heavy inclusion diamonds or diamond filled with lots of impurities. These impurities or the heavy inclusions givesthe diamonds its unique color. That is the main reason they are often opaque. Despite all this impurities and varied colors, these diamonds have their own charm.They are mostly found with some of the newest jewelry designers in the market.
Icy Diamonds are new variety of diamonds that emerged recently.Also known as rough, uncut, specimen grade, industrial, cloudy, decorative industrial or just a plain borts. They are very popular.
The introduction of black diamonds in last nineties have made cocktail jewellery very popular. Black diamonds find their place with many of Hollywood celebrities. They are used in making swiss watch.
Icy Diamonds don’t have a brilliant cut. They are made mostly in pear shape, round shape, oval shape and fancy rose cut shapes. As a nice diamond manufacturer, George Diamonds have got varied sizes from: 0.30 carat to almost 5 carats normally. We also manufacture any size, shape, and color diamonds depending on the rough availability.
Colors available are cloudy white, yellow, grey, red brown, greenish brown, light yellow, and others. Jewelers also use them in combinations with lower quality white diamonds.
Icy Diamonds or uncut jewelry diamonds are often used in combination with many gemstones like ruby, sapphire and emerald. As the one of the biggest ice diamond manufacturer, we often use it in single stone jewelry using either 925 sterling silver or 14k white/yellow gold to give a classic pattern to a ring.
We also use icy diamond in pendants, earrings and bracelets.
The price of these diamonds are much lower than their white counterparts or even black diamonds.
It is made using industrial rough diamonds or borts, which lowers the price. If anybody would like to wear unique jewelry, like a classic and vintage look, Ice diamonds is the best option. Ice diamonds are available in many colors, sizes and quality.

Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high quality, high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films.
HPHT stands for high pressure and high temperature. It is a method of applying HPHT to those diamonds that are not fully crystallized (“premature diamonds”) when released from fiery, erupting volcanoes. The HPHT process is a scientific procedure that is carefully controlled.
Recently, there has been much debate over what exactly CVD and HPHT diamonds are. What is the difference between the synthetic, man-made diamond, and an HPHT diamond, from Mother Nature?
CVD diamonds are simply lab created synthetic diamonds. The initials stand for “Controlled Vapor Diffusion.” This is a process done in a controlled laboratory which creates the exact physical and chemical properties of a natural diamond. HPHT stands for “High Pressure High Temperature.” These are natural diamonds, from Mother Nature, whose colour has been improved. HPHT diamonds are processed in a controlled laboratory, and put under extreme heat, and pressure, which changes the colour of the diamond from a brownish tint to white. Diamonds that are subjected to the HPHT treatment must have a clarity of VS1 or better.
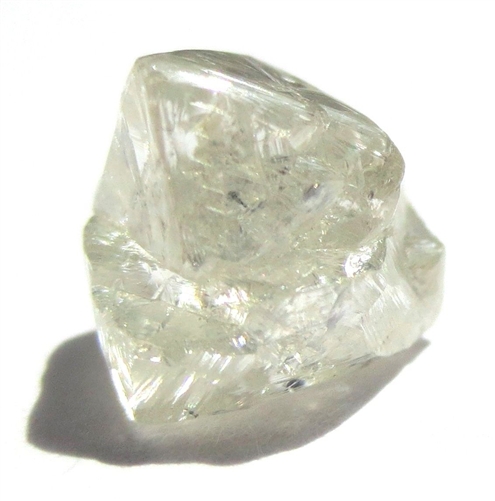

Made from carbon, diamonds are the hardest known substance to man and are both a naturally occurring and manufactured abrasive. Natural diamonds form at high pressure high temperature conditions, and are found between 85 to 125 miles in the earth’s mantle. It takes a diamond 1 to 3 billion years to form beneath the earth. Once formed, a diamond travels to the earth’s surface via streams of molten rock. Throughout this process, natural diamonds acquire inclusions and or flaws within them that give them their own unique “fingerprint”.
Diamonds can be purchased in various sizes (carats), shapes, colors, and clarities. Natural diamonds are preferred over enhanced or treated diamonds because of their rarity and individual fingerprint. No two natural diamonds in the world are identical; each one is unique whether it’s because of its color or clarity or both combined.

The term “enhanced” may sound like a positive feature, but, any diamond can be enhanced or treated and altered from its natural condition to artificially improve its appearance. It is done to them to improve their characteristics, or their natural “flaws”If you decide to purchase an “enhanced” diamond, verify the kind of treatments used and how they would affect the value of the diamond, long term care and appearance.
These enhancement treatments sometimes result in discoloration or cracks in the diamond.
One type of treatment is laser drilling, which removes minor inclusions in a diamond to produce a clarity enhanced diamond. This process will typically create lines that resemble tiny trails, visible only under side-view magnification. The laser may dissipate the imperfection, or chemicals may be injected to bleach away the color. This is a more permanent process than fracture filling. However, it is highly debated whether or not this process damages the integrity of the diamonds, thereby decreasing the value of clarity enhanced diamonds in the long term.
Fracture filling is a treatment that adds a glass-like resin material to a natural diamond to close small cracks. Since the filling has the same optical illusion and refraction index as a natural diamond, it’s nearly impossible to detect the “repair” to the flaws. Fracture filling is not a permanent treatment as heat from future repairs, cleanings, and even sunlight can erode the filler or possibly darken its color, making the diamond less valuable as time goes on.
Other type of enhancement treatment is called HPHT (high-pressure high-temperature). HPHT is a treatment process that General Electric developed to permanently change the color of a diamond. First used to turn yellowish diamonds into “fancy” colored diamonds, this process is commonly used to turn yellow or brown diamonds into colorless diamonds to be sold at a significantly higher prices. HPHT involves putting a diamond into a pressure chamber and squeezing it at high pressure and high temperature for a short amount of time. This treatment is debated as some feel that it is a standard technique, but the Federal Trade Commission feels that it is an artificial process and requires that HPHT be disclosed. When HPHT treatment is detected in a diamond, the Gemological Institute of American (GIA) notes it on their reports as “HPHT Annealed” or “Artificially Irradiated” and insists that such diamonds be laser-inscribed with the same designation. A diamond that has been enhanced by GE will be inscribed with the symbol “GE POL”.

The idea of making artificial diamond isn’t new. Scientists have come up with ways to create synthetic diamonds and diamond simulants like cubic zirconia In the past decade, scientists have perfected a technique called Chemical Vapor Deposition, where carbon gas cloud is passed over diamond seeds in a vacuum chamber heated to more than 1,800 degrees. In a few days, the diamonds are virtually indistinguishable from natural ones, even to the experts:
Price of diamond will not fall. Companies that make cultured diamonds like Apollo and Gemesiswill not flood the market with cheap stones.
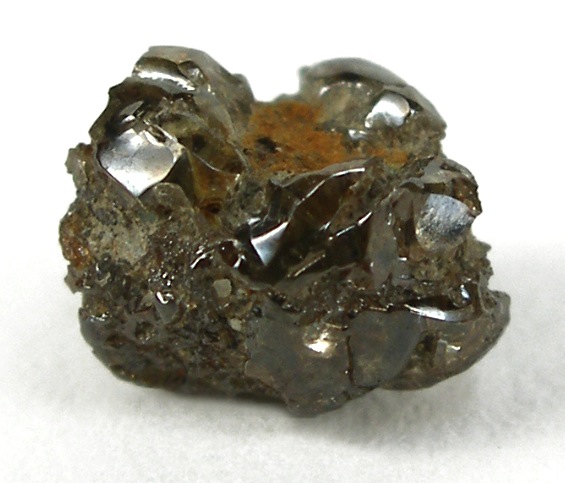

Bort or boart is a non-familiar word used in the diamond industry which refers to shards of non-gem-grade quality diamonds. In the manufacturing and heavy industries, “bort” is used to describe dark, imperfectly formed crystallized diamonds of varying levels of opacity. The lowest grade, “crushing bort”, is crushed by steel mortars and used to make industrial-grade abrasive grits. Small bort crystals are used in drill bits. 75% of the world’s supply of crushing bort are from TheDemocratic Republic of the Congo.